| Atomic-scale insights into the ion-diffusion induced degradation for silicon heterojunction solar cells【俞健】 |
| 发布时间:2025-09-25 | 浏览次数:343 |
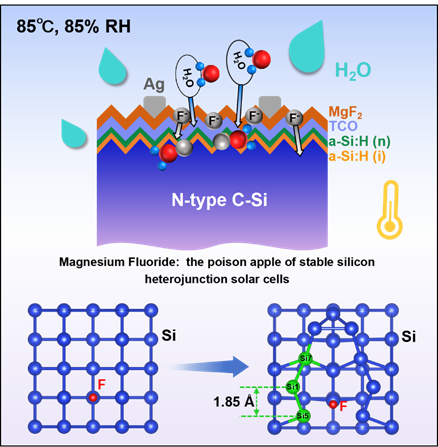
Atomic-scale insights into the ion-diffusion induced degradation for silicon heterojunction solar cells 俞健1*, 白宇1, 罗红1, 张一民2, 刘文柱3, 孟胜4 1 西南石油大学新能源与材料学院 2 郑州大学物理学院/教育部材料物理重点实验室 3 中国科学院上海微系统与信息技术研究所 4 中国科学院物理研究所 *E-mail: jianyu@swpu.edu.cn Abstract Metal-based halogen compounds, represented by MgF2, are widely used in many advanced photovoltaic technologies, not only playing a key role in passivating contacts, but also acting as an excellent anti-reflective layer. However, we found the MgF2 layer for silicon solar cells was a double-edged sword during the damp-heat (DH) stability test, resulting in a sharp reduction in Eff of 53.5 rel.% after only 200 h. The interaction between MgF2 in ionic form and water leads to corrosion of the Si surface, resulting in lattice defects in the c-Si and severely deteriorated a-Si:H/c-Si(n) interface. We employ SiO2 thin films, which efficiently suppress degradation, ensuring long-term stable operation of solar cells in DH environments.
|